New Delhi
Liver failure is the inability of the liver to perform its normal synthetic and metabolic functions.
Liver failure occurs when large parts of the liver become damaged beyond repair and the liver is no longer able to function. In liver failure or hepatic insufficiency there is inability of the liver to perform its normal synthetic and metabolic function as part of normal physiology.Liver failure is a life-threatening condition that demands urgent medical care.
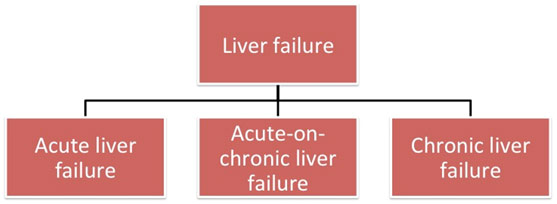
Acute liver failure (ALF), also known as fulminant hepatic failure (FHF), is loss of liver function that occurs rapidly — in days to weeks —in a person who has no pre-existing liver disease. ALF can cause serious complications, including excessive bleeding and increasing pressure in the brain. It is a medical emergency that requires urgent hospitalization. Common causes of ALF are: acute viral hepatitis, drug-induced liver injury, paracetamol overdose, autoimmune liver disease etc.
Acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) is an increasingly recognized entity encompassing an acute deterioration of liver function in patients who already has cirrhosis, which is usually associated with a precipitating event and results in the failure of one or more organs and high short-term mortality. Common precipitants for development of ACLF are viral hepatitis, alcohol, and bacterial infections. ACLF is potentially reversible if the precipitating cause is removed.
Chronic liver failure, also called end-stage liver disease, may take from several months to many years to develop. It is usually the result of slow and progressive deterioration of liver functions in patients with liver cirrhosis of any cause. Compared to ACLF the progression to liver failure in chronic liver failure is slow, taking months to years, and it is irreversible.
Depending on the cause, ALFand ACLF can sometimes be reversed with treatment. In many situations, though, a liver transplant may be the only cure. For chronic liver failure the only treatment option is liver transplantation.
Acute liver failure and acute-on-chronic liver failure are potentially reversible, while chronic liver failure is irreversible.